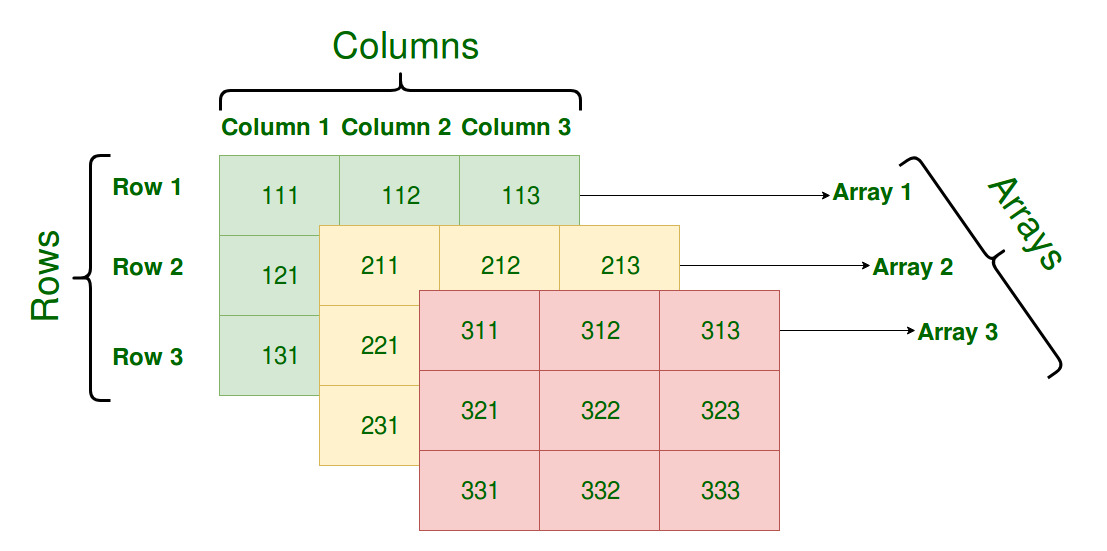
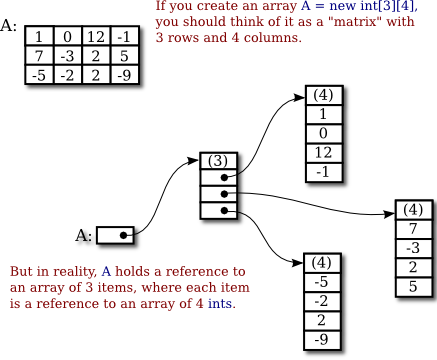
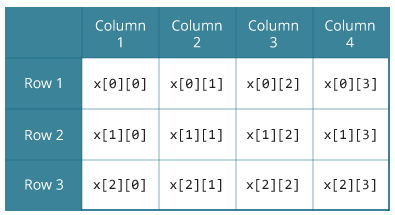
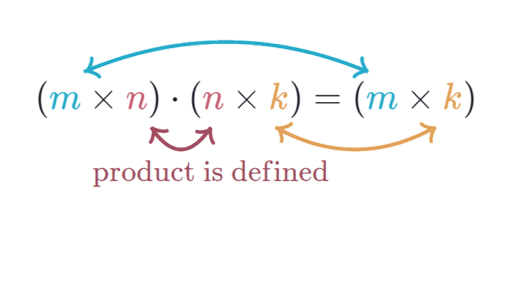When referring to a specific value in a matrix called an element a variable with two subscripts is often used to denote each element based on their position in the matrix.
Finding the dimensions of a matrix.
A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m n matrix or m by n matrix while m and n are called its dimensions.
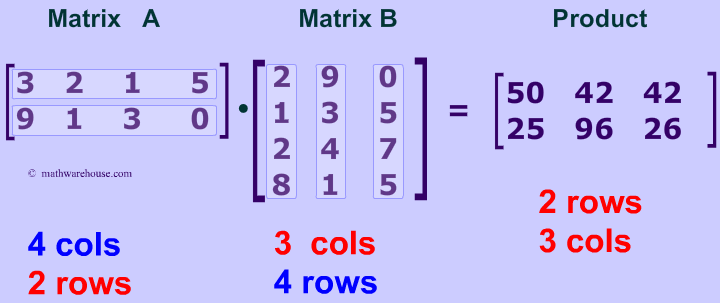
Find the matrix determinant the rank raise the matrix to a power find the sum and the multiplication of matrices calculate the inverse matrix.
This means that a has m rows and n columns.
Since a has three rows and four columns the size of a is 3 4 pronounced as three by four.
The columns go up and down.
For example if a is a 3 by 4 matrix then size a returns the vector 3 4.
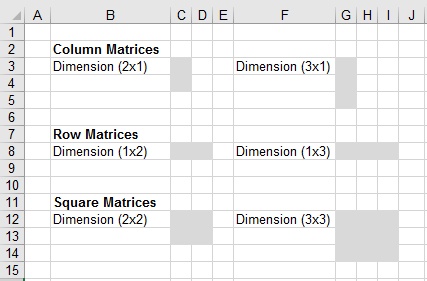
Leave extra cells empty to enter non square matrices.
The dimension is the number of bases in the column space of the matrix representing a linear function between two spaces.
Here is a matrix with three rows and two columns.
Sometimes the dimensions are written off to the side of the matrix as in the above matrix.
The rows go side to side.
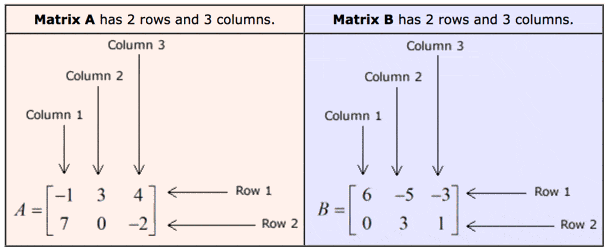
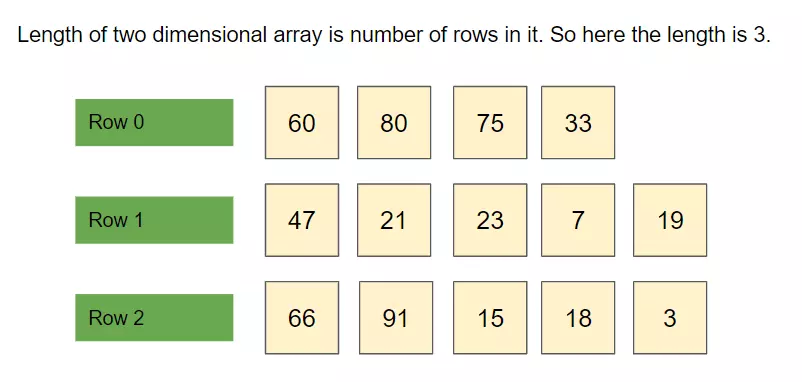
The size of a matrix is defined by the number of rows and columns that it contains.
With help of this calculator you can.
For instance consider the following matrix a.
If a is a table or timetable then size a returns a two element row vector consisting of the number of rows and the number of table variables.
Google classroom facebook twitter.
The dimensions of a matrix a are typically denoted as m n.
The numbers of rows and columns of a matrix are called its dimensions.
Sz size a returns a row vector whose elements are the lengths of the corresponding dimensions of a.
If you have a linear function mapping r3 r2 then the column space of the matrix representing this function will have dimension 2 and the nullity will be 1.
The dimensions for a matrix are the rows and columns rather than the width and length.
But this is just a little reminder and not actually part of the matrix.